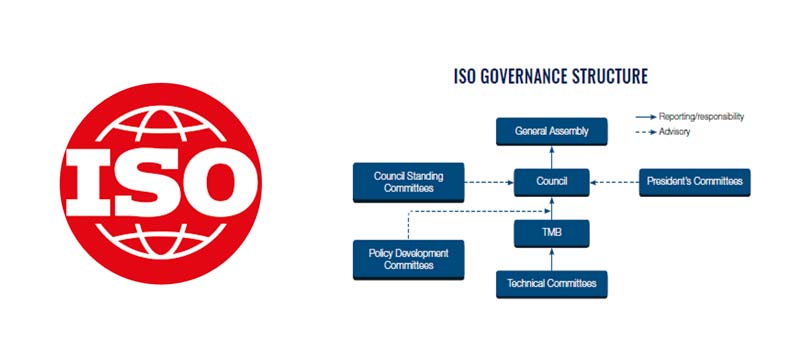
ISO Structure
Members
- 161 standards bodies Represent ISO in their respective countries
- Approve standards by voting
- Enable national experts and stakeholders to participate in standards development
ISO Central Secretariat
- 150 staff
- Facilitates participation in standardization and partner relations
- Coordinates standards development and makes them available
- Provides neutral platform to achieve consensus
Technical Committees
- More than 100,000 Experts
- Nominated by members
- Can come from partner organizations
- Participate in Technical Committees
- Write the standards.
ISO Technical Committee operatation
ISO organizes technical committees comprising experts representing most sectors of society. There are currently more than 250 ISO technical committees.
Experts that develop ISO Standards have the knowledge and experience to understand and anticipate the challenges within their particular sector, including how standardization can create a level playing field that benefits everyone.
Technical committees develop strategic business plans, which analyse market needs and demonstrate how they will be addressed by the work of the technical committee.
ISO members choose whether they want to be part of a particular technical committee (TC) and their level of involvement. Observing members (O-members) can observe the standards that are being developed, offering comments and advice. Participating members (P-members) actively participate by voting on the standard at various stages of development.
ISO’s technical work is managed by the Technical Management Board (TMB). TMB tasks include setting up technical committees, appointing chairs and monitoring the progress of technical work. The TMB reports to the ISO Council.
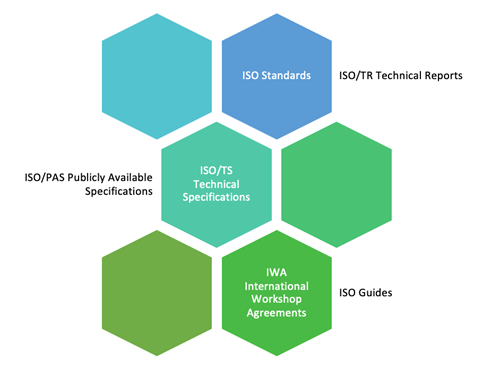
ISO Products
ISO Standards
- International standards provide rules, guidelines or characteristics for activities, or their results, aimed at achieving an optimum degree of order and consistency in a specific context.
- Can take many forms, including product standards, guideline standards, management systems standards, test methods, and codes of practice.
ISO/TR Technical Reports
- Technical reports contain useful information and data that may be obtained from a survey or an informative report on the perceived “state of the art” within a given context.
ISO/TS Technical Specifications
- Technical specifications address specific technical areas where the possibility exists to reach future agreement on an International Standard.
- Published for immediate use, providing a means to obtain feedback.
- Aim is to eventually transform and republish the Technical Specification as an International Standard.
ISO/PAS Publicly Available Specifications
- Publicly available specifications are published for immediate use, providing a means to obtain feedback for eventual transformation into an International Standard.
- Respond to an urgent market need, representing either a consensus of the experts within a working group, or in an organization external to ISO.
ISO International Workshop Agreements
- International workshop agreements are prepared through a workshop mechanism outside of ISO committee structures.
- Intended to ensure broad participation of relevant interested parties worldwide.
- Responds to urgent market requirements.
- Approved by consensus.
- If there is an existing ISO committee whose scope covers the topic, the published IWA is automatically allocated to this committee for maintenance.
ISO Guides
- Guides help stakeholders understand more about the main areas where standards add value, including how and why ISO standards can make things work better, safer, and more efficiently. A full list of Guides is available in the ISO Catalogue
ISO Client benefits
Industry
- Competitiveness
- Increased quality and safety
- Market acceptance
- Greater efficiency
Investment
- Sustainable investment
- Interoperability
- Innovation
Regulators
- Increased global trade
- Credibility and trust throughout the supply chain
Society
- Actions to address global challenges
- Greater choice
- Platform to achieve consensus.